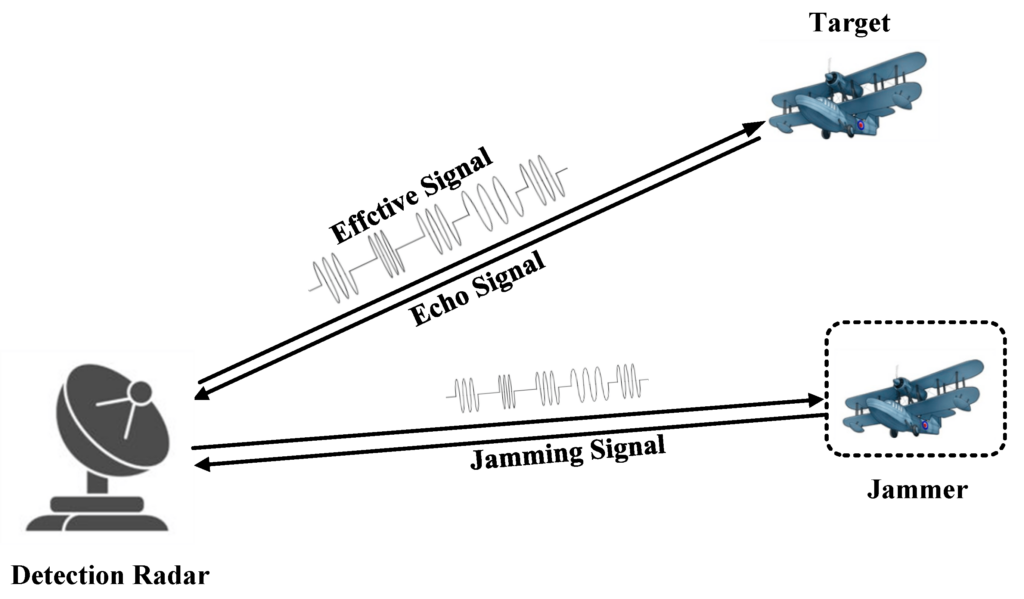
INTRODUCTION:
Quantum radar jamming systems represent the next generation of electronic warfare technology, leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics to detect, track, and counteract stealth technologies. Unlike conventional radar systems that rely on radio waves, quantum radars use entangled photons to detect objects with enhanced accuracy and resilience against traditional jamming techniques. As quantum technology advances, the development of quantum radar jamming systems becomes essential for maintaining strategic military superiority, especially in the context of modern stealth aircraft and electronic countermeasure systems.
TECHNOLOGY USED:
1.Quantum Radar Principles:
- Quantum Entanglement: Utilizes pairs of entangled photons. When one photon is transmitted and interacts with an object, its entangled twin, kept at the radar base, reflects the interaction, allowing for precise detection even in noisy environments.
- Quantum Illumination: A method that uses entangled photon pairs to improve target detection amidst background noise, enhancing sensitivity and range.
2. Quantum Jamming Techniques:
- Quantum Decoherence Attack: Disrupts the entanglement of photons, rendering the quantum radar ineffective by introducing environmental noise.
- Quantum Signal Spoofing: Mimics the entangled photon signals to create false targets or confuse the radar system.
- Interference with Quantum Communication Channels: Targeting the communication channels that relay quantum information between the radar and control systems.
3. Hardware and Components:
- Single-Photon Sources and Detectors: Essential for generating and detecting entangled photons with high precision.
- Quantum Memory: Stores quantum states for processing and analysis, enabling complex jamming algorithms.
- Cryogenic Systems: Required for maintaining the stability of quantum states by reducing thermal noise.
4. Software and Algorithms:
- Quantum Noise Filtering Algorithms: Used to distinguish genuine signals from quantum jamming noise.
- Machine Learning Integration: Enhances pattern recognition and adaptive response against evolving jamming techniques.
- Quantum Cryptography: Ensures secure communication between radar systems and control units.
APPLICATIONS:
- Military and Defense:
- Stealth Detection and Countermeasures: Quantum radars can detect stealth aircraft and low-observable vehicles, making traditional jamming techniques obsolete. Quantum jamming systems counteract this by disrupting the quantum entanglement process.
- Electronic Warfare: Quantum jamming systems are designed to neutralize enemy quantum radars, protecting high-value assets and enhancing survivability.
- Secure Communications: Quantum cryptography ensures secure data transmission between radar systems and command centers, resistant to conventional electronic eavesdropping.
- Aerospace and Aviation:
- Anti-Stealth Technology: Quantum radars can detect low-RCS (Radar Cross Section) targets, prompting the need for advanced jamming systems to protect stealth aircraft.
- Navigation and Guidance Systems: Quantum jammers can disrupt quantum navigation systems, affecting enemy missile guidance and UAV operations.
- Cybersecurity and Intelligence:
- Quantum Signal Interception: Quantum jammers can intercept and manipulate quantum communication signals, providing strategic intelligence and counter-surveillance capabilities.
- Quantum Cryptography Attacks: Advanced quantum jammers can potentially break quantum encryption protocols, leading to new cybersecurity challenges.
CHALLENGES AND LIMITATION:
- Technical Complexity: Building and maintaining stable quantum systems requires advanced technology and expertise.
- Cost and Infrastructure: Quantum systems are expensive, and deploying them at scale requires substantial infrastructure investment.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Quantum states are highly sensitive to environmental noise, requiring sophisticated shielding and cryogenic cooling.
- Ethical and Legal Concerns: The use of quantum radar jamming systems in warfare raises ethical questions and may require new regulations in international military law.
FUTURE PROSPECTS:
- Development of Quantum-Resilient Systems: As quantum jamming technologies evolve, so will quantum radar systems, leading to an ongoing arms race in electronic warfare.
- Integration with AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing adaptive jamming strategies and improving detection accuracy.
- Global Arms Control Considerations: International treaties and regulations may emerge to control the development and deployment of quantum jamming technologies.
CONCLUSION:
Quantum radar jamming systems represent a revolutionary shift in electronic warfare, challenging the capabilities of modern stealth technology and secure communications. As quantum computing and communication technologies advance, these systems will become more sophisticated, necessitating continuous innovation and strategic planning in defense sectors worldwide.
