Introduction
Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarm technology has emerged as a groundbreaking development in the field of robotics and autonomous systems. This technology enables multiple drones to work together as a coordinated unit, mimicking the behavior of natural swarms like birds or insects. As we step into 2025, UAV swarming algorithms have become increasingly sophisticated, offering unprecedented capabilities in both civilian and military applications.

How They Work
UAV swarming algorithms are the backbone of swarm intelligence in drone operations. These algorithms enable individual drones to communicate, coordinate, and make collective decisions. Here’s how they work:
- Distributed Decision-Making: Each drone in the swarm is equipped with algorithms that allow it to make independent decisions based on local information and shared data from other swarm members.
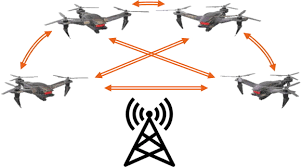
- Consensus Algorithms: Protocols like Raft ensure synchronization of drone actions and maintain decision consistency across the network, even in the event of communication disruptions.
- Self-Organization: Advanced algorithms allow drones to adapt to environmental changes, restore connections, and coordinate actions with other drones autonomously.
- Swarm Navigation and Control: These algorithms enable precise formation flying and efficient coordination among swarm members.
- AI and Machine Learning Integration: Intelligent algorithms facilitate autonomous decision-making, improved object recognition, obstacle detection, and optimized flight paths.
Advantages
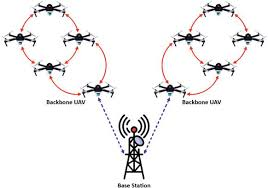
- Enhanced Mission Capabilities: Swarms can cover larger areas and perform complex tasks more efficiently than individual drones.
- Resilience and Redundancy: The loss of one or more drones doesn’t compromise the overall mission, as the swarm can adapt and redistribute tasks.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Swarms of smaller, cheaper drones can potentially replace or supplement more expensive, traditional systems.
- Scalability: Swarm algorithms are designed to work with varying numbers of drones, allowing for easy scaling of operations.
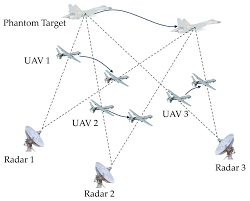
- Versatility: UAV swarms can be applied to various fields, including search and rescue, environmental monitoring, and precision agriculture.
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Developing and implementing effective swarming algorithms is challenging and requires advanced expertise.
- Communication Vulnerabilities: Swarms rely heavily on communication, making them potentially vulnerable to jamming or interference.
- Ethical Concerns: The use of autonomous swarms, especially in military applications, raises ethical questions about decision-making and accountability.
- Regulatory Challenges: Existing regulations may not adequately address the unique aspects of swarm operations, potentially limiting their deployment.
- Resource Intensive: Managing and coordinating large swarms requires significant computational resources and energy.
Future Scope
The future of UAV swarming algorithms is bright and filled with potential:
- Advanced AI Integration: Further integration of AI and machine learning will enhance swarm decision-making capabilities and adaptability.
- Heterogeneous Swarms: Development of swarms comprising drones with diverse capabilities for more specialized and efficient task allocation.
- Improved Energy Efficiency: Research into more energy-efficient algorithms and hardware to extend mission durations.
- Enhanced Autonomy: Progress towards swarms that can operate with minimal human intervention, even in complex and dynamic environments.
- Interdisciplinary Applications: Expansion into new fields such as environmental conservation, urban planning, and disaster response.
- Swarm-Human Interaction: Development of intuitive interfaces for humans to interact with and control swarms effectively.
As we look towards the future, UAV swarming algorithms continue to evolve, promising to revolutionize various industries and open up new possibilities in autonomous operations. The ongoing research and development in this field will undoubtedly lead to more sophisticated, efficient, and versatile swarm systems, shaping the landscape of drone technology in the years to come.
