
Introduction:
Tidal lagoon power plants are a form of renewable energy technology that harnesses the power of the ocean’s tides to generate electricity. The basic concept behind tidal lagoon plants is to trap water inside a lagoon created by a barrier, which is then released through turbines to generate energy. This technology is part of the growing interest in marine energy, which seeks to utilize the natural movement of water to provide a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuel-based energy sources. As the world looks to combat climate change and reduce its reliance on non-renewable energy sources, tidal lagoon power plants present a promising solution for cleaner energy production.
How It Works:
The working principle behind tidal lagoon power plants revolves around the use of the predictable motion of tides to generate energy. The process involves the following steps:
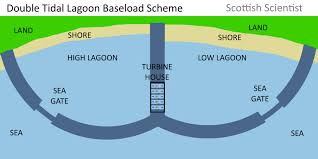
- Construction of the Lagoon: A tidal lagoon is created by building a large barrier or seawall around a section of the coastline, forming an enclosed water body. This lagoon can vary in size, depending on the specific energy generation capacity desired.
- Tidal Movement: As the tide rises and falls, water flows in and out of the lagoon. This tidal movement causes fluctuations in the water level inside the lagoon, creating potential energy.
- Energy Generation: At the entrance of the lagoon, turbines are installed, and these turbines are connected to generators. When the tide rises, water is trapped inside the lagoon. As the tide recedes, the water is released through the turbines, causing them to spin and generate electricity.
- Power Transmission: The electricity generated is then transmitted through cables to the grid, where it can be distributed for use by homes, businesses, and industries.
Technology Used:
Several key technologies are used in the construction and operation of tidal lagoon power plants:
- Turbines: These are the heart of the energy generation process. Similar to those used in traditional hydroelectric plants, turbines are designed to spin as water moves through them. Some tidal lagoon plants may use traditional hydro turbines, while others may employ more advanced technologies, such as vertical-axis turbines or oscillating water columns.
- Lagoon Barrage: The barrier or seawall that forms the lagoon is typically made from materials such as concrete or steel, designed to withstand the impact of the tidal forces and provide long-lasting durability.
- Control Systems: Modern tidal lagoon plants incorporate advanced control systems that monitor and manage the inflow and outflow of water, optimizing the power generation process while ensuring the structural integrity of the lagoon.
- Energy Storage: In some designs, energy storage systems are used to store excess energy generated during periods of high tide and release it during periods of low tide, allowing for a more consistent power supply.
Advantages:
Tidal lagoon power plants offer a variety of benefits, making them a promising option for future energy production:
- Renewable and Sustainable: Tidal energy is renewable, as tides are predictable and constant, driven by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun. Unlike wind or solar power, tidal energy can be forecasted accurately, providing a stable energy source.
- Low Environmental Impact: Tidal lagoon plants have a minimal environmental footprint compared to fossil fuel-based power plants. They do not produce emissions or pollution, contributing to a cleaner, healthier environment.
- High Energy Efficiency: The energy density of tidal movements is relatively high, and the potential for generating electricity is significant, especially in areas with large tidal ranges.
- Coastal Protection: The lagoon structure itself can act as a barrier against coastal erosion, protecting shorelines from storm surges and sea-level rise caused by climate change.
- Job Creation: The construction, operation, and maintenance of tidal lagoon power plants can generate local employment opportunities in coastal regions.
Disadvantages:
Despite their potential, tidal lagoon power plants also have a number of challenges and disadvantages:
- High Initial Costs: The construction of a tidal lagoon plant involves significant upfront costs, including the building of barriers and infrastructure, which can be a major financial barrier.
- Environmental Impact: Although tidal energy is considered eco-friendly, the construction of a lagoon can have an impact on local ecosystems, especially marine life. The disruption of tidal flows could affect fish migration patterns and local biodiversity.
- Limited Site Availability: Tidal lagoon plants require specific conditions, such as strong tidal currents and suitable coastal geography. Suitable sites for such plants may be limited, restricting their widespread use.
- Intermittency of Power: While tidal energy is predictable, it is still intermittent, as energy can only be generated when the tide is flowing in or out. This requires storage or backup systems to ensure a continuous supply of energy.
- Long Construction Time: Building a tidal lagoon plant can take several years due to the complexity of the project and potential environmental permitting processes.
Future Scope:
The future of tidal lagoon power plants looks promising, but several factors need to be addressed for them to become a mainstream energy solution:
- Technological Advancements: Continued research into more efficient turbines and energy storage systems can improve the overall performance of tidal lagoon plants, making them more competitive with other forms of renewable energy.
- Cost Reduction: As the technology matures and economies of scale come into play, the cost of constructing and operating tidal lagoon plants is expected to decrease, making them a more financially viable option.
- Global Expansion: With suitable coastal locations in countries around the world, tidal lagoon plants could become a significant part of the global energy mix. Governments may also offer incentives for clean energy projects, encouraging the development of tidal power.
- Integration with Other Renewables: Tidal lagoon power could be integrated with other renewable sources, such as solar and wind, to create a more diverse and resilient energy system. The combination of tidal energy’s predictability with the intermittent nature of other renewables could provide a more balanced and sustainable power grid.
- Environmental Mitigation: As environmental concerns are a significant barrier to the adoption of tidal lagoon plants, future developments may focus on designing systems that minimize their ecological impact, such as fish-friendly turbines and better management of the surrounding habitats.
