SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY:
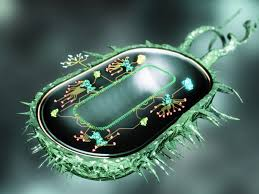
Synthetic biology is a field of science that involves redesigning organisms for useful purposes by engineering them to have new abilities. Synthetic biology researchers and companies around the world are harnessing the power of nature to solve problems in medicine, manufacturing and agriculture.
KEY TECHNOLOGIES:
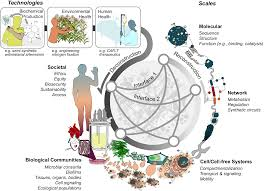
Synthetic biology combines engineering principles with existing biotechnology techniques, such as DNA sequencing and genome editing, to modify organisms or create new ones.
ADVANTAGES:
The advantages of biotechnology can range from the reduction of environmental pollution to its involvement in medical and industrial processes, among other things. However, when biotechnology is mishandled, it can result in the emergence of a variety of problems.
DISADVANTAGES:
Disadvantages of biotechnology: Ethical concerns, such as the use of genetically modified organisms. Possibility of unintended consequences. High costs for research and development.
USES:

Biotechnology had a significant impact on many areas of society, from medicine to agriculture to environmental science. One of the key techniques used in biotechnology is genetic engineering, which allows scientists to modify the genetic makeup of organisms to achieve desired outcomes.
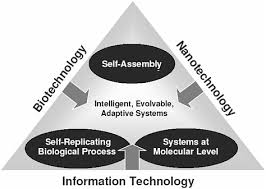
HOW IT WORKS:
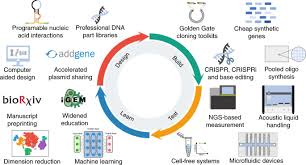
Biotechnology is the use of an organism, or a component of an organism or other biological system, to make a product or process. Many forms of modern biotechnology rely on DNA technology. DNA technology is the sequencing, analysis, and cutting-and-pasting of DNA.
