SMART CITIES:
A smart city is a city that uses digital technology to improve services, manage infrastructure, and increase efficiency. The goal is to improve quality of life for citizens, promote economic growth, and reduce emissions.
How smart cities work
- Data collection: Smart cities collect data from devices, buildings, citizens, and cameras.
- Data analysis: Data is analyzed to monitor, plan, and govern the city.
- Technology: Smart cities use technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
- Integration: Smart cities integrate people, technology, and processes across sectors like transportation, healthcare, and education.
Examples of smart city applications
- Transportation: Traffic and transportation systems
- Waste management: Optimizing waste collection routes to reduce emissions
- Public safety: Analyzing data from security cameras and connected devices to detect crime
- Energy: Improving energy efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions
Smart city history
- The term “smart city” may have originated with Amsterdam’s De Digital Stad (DDS) in 1994. DDS was a free net that improved communication between residents and the government.
Smart city initiatives in India
- India has a Smart Cities Mission to improve the lives of urban citizens and drive economic growth.

KEY TECHNOLOGIS:
Smart cities use a variety of technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing to improve city services and sustainability.
Artificial intelligence (AI)
- Uses machine learning to solve problems
- Analyzes data from security cameras and connected devices to help law enforcement
- Optimizes waste collection routes to reduce carbon emissions
- Establishes new connections for gas, electricity, and water
Internet of Things (IoT)
- A network of physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies
- Collects information about the condition of roads, buildings, water bodies, and bridges
- Monitors and controls traffic
- Optimizes maintenance
- Improves public safety
Cloud computing Provides services for smart cities.
Other technologies Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), Machine-to-Machine Communications, Mesh Networks, Big data analytics, and 5G technologies.
Smart cities use these technologies to create a seamless, connected environment where everything operates more efficiently. The goal is to build urban spaces that are more livable, resilient, and ready for future challenges.

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF SMART CITIES:
Smart cities can have many benefits, including improved public health, transportation, and the environment. However, they can also have disadvantages, such as privacy concerns and financial challenges.
Benefits
- Improved public health Smart cities can use connected devices and software to improve public health.
- Efficient transportation Smart cities can use traffic management systems to reduce congestion and improve commuting efficiency.
- Environmental benefits Smart cities can use energy-efficient buildings, air quality sensors, and renewable energy sources to reduce their ecological impact.
- Digital equity Smart cities can enable citizens to input data regarding public and private services through mobile devices.
- Improved community safety Smart cities can use applications to help fight crime and improve other aspects of public safety.
Disadvantages
- Privacy concerns: Smart cities can affect privacy.
- Financial challenges: Smart cities can require significant financial investments for implementation, maintenance, and upgrades.
- Social control: Smart cities can allow authorities to track and centralize information gathered by security cameras, which could lead to social control.

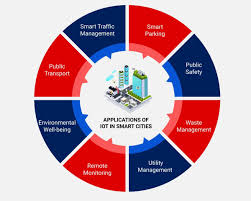
USES OF SMART CITIES:
Smart cities utilize digital technologies to optimize various urban functions, including traffic management, energy consumption, waste disposal, public safety, water management, and citizen engagement, aiming to improve quality of life by collecting and analyzing data through connected devices and sensors across the city infrastructure, ultimately leading to more efficient and sustainable urban environments.
Key uses of smart cities include:
- Transportation Management:
- Real-time traffic monitoring and signal adjustments to reduce congestion.
- Smart parking systems to locate available parking spaces.
- Optimized public transportation routes and schedules.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Smart grids to monitor and manage energy consumption in buildings and across the city.
- Intelligent street lighting that adjusts brightness based on conditions.
- Renewable energy integration and monitoring.
- Water Management:
- Leak detection in water pipes using sensors.
- Real-time water usage monitoring and optimization.
- Water quality monitoring systems.
- Waste Management:
- Smart waste bins that monitor fill levels and optimize collection routes.
- Recycling tracking and incentive programs.
- Public Safety:
- Video surveillance systems with facial recognition capabilities.
- Emergency response systems with real-time location tracking.
- Crime hotspot analysis and predictive policing.
- Citizen Engagement:
- Online platforms for reporting issues and providing feedback to the government.
- Interactive maps and data visualization tools for citizen access to city information.
- Digital platforms for community engagement and participation.
Key technologies used in smart cities:
- Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors and devices connected to the internet to collect real-time data.
- Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large datasets to identify patterns and trends for informed decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: Storing and processing large volumes of data on remote servers.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Visualizing geospatial data to understand spatial relationships