
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automobile industry by offering a cleaner and more energy-efficient alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. However, one of the biggest challenges EVs face is charging infrastructure and battery limitations. To overcome this, researchers and companies are working on self-charging electric vehicles, which can generate their own energy through solar power, regenerative braking, and wireless charging roads. This innovation could make EVs more efficient, convenient, and environmentally friendly.
How Do Self-Charging Electric Vehicles Work?
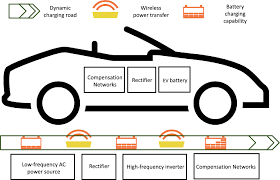
Self-charging EVs use a combination of advanced energy-harvesting technologies to reduce dependency on external charging stations. Some key technologies include:
- Solar Panel Integration
- Solar panels are embedded into the roof, hood, and trunk of the car.
- They convert sunlight into electricity, which charges the battery while the car is parked or in motion.
- Example: Lightyear 0, a solar-powered EV, can generate energy for up to 70 km (43 miles) per day in optimal sunlight.
- Regenerative Braking
- When the driver brakes, the car’s kinetic energy is converted into electrical energy.
- This energy is stored in the battery for later use.
- Most modern EVs, including Tesla, Nissan Leaf, and Toyota hybrids, already use this technology.
- Wireless Charging Roads
- Special inductive charging coils are embedded in the roads.
- As the vehicle moves over these roads, electricity is transferred wirelessly to the EV’s battery.
- Countries like Sweden and Israel are currently testing wireless charging highways.
- Kinetic Energy Harvesting
- The movement of wheels or vibrations from driving can be converted into electricity using piezoelectric materials.
- This technology is still in development but could further improve energy efficiency.
Current Developments in Self-Charging EVs

🔹 Aptera Motors is developing a solar-powered EV that claims to run up to 1,000 miles per charge using solar energy.
🔹 Toyota and Hyundai are experimenting with integrating solar roofs into their EV models.
🔹 Electreon, an Israeli startup, has developed wireless charging roads that can power EVs while they drive.
🔹 Tesla has hinted at future advancements in solar-integrated charging.
Potential Benefits of Self-Charging EVs

✅ Reduced Charging Dependency – Less need for charging stations, making EVs more convenient.
✅ Longer Driving Range – Cars can extend their range by generating energy while in motion.
✅ Lower Carbon Footprint – Self-charging EVs rely on renewable energy sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
✅ Cost Savings – Owners can save money on electricity and charging fees.
✅ Enhanced Sustainability – Combines multiple clean energy technologies for a greener future.
Challenges & Limitations

🔴 Limited Solar Efficiency – Solar panels can only generate a small fraction of the energy needed for daily driving.
🔴 Weather Dependency – Cloudy or rainy conditions reduce the efficiency of solar charging.
🔴 High Development Costs – Wireless charging roads and kinetic energy harvesting require significant investment.
🔴 Battery Wear & Tear – Constant charging and discharging cycles could impact battery lifespan.
Expected Launch Timeline

- 2025-2027 – Advanced solar-powered EVs with extended range and better energy efficiency.
- 2030+ – Wireless charging roads and fully integrated self-charging EVs may become more widespread.
Conclusion
Self-charging electric vehicles represent a significant step toward a sustainable, carbon-free future. By combining solar power, regenerative braking, wireless charging, and kinetic energy harvesting, these vehicles could revolutionize transportation by making EVs more autonomous and energy-efficient. While challenges like weather dependency and infrastructure costs remain, continuous advancements in technology are bringing us closer to a world where electric vehicles can charge themselves on the go.
Would you like more details on a specific aspect? 🚗⚡
