Introduction
Microwave-powered drones represent a groundbreaking advancement in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) technology. As we step into 2025, these innovative drones are poised to revolutionize various sectors, from military applications to civilian uses such as long-duration surveillance, disaster response, and telecommunications. By harnessing the power of microwaves for propulsion and energy, these drones overcome many limitations of traditional battery-powered UAVs, offering extended flight times and enhanced capabilities.
How They Work
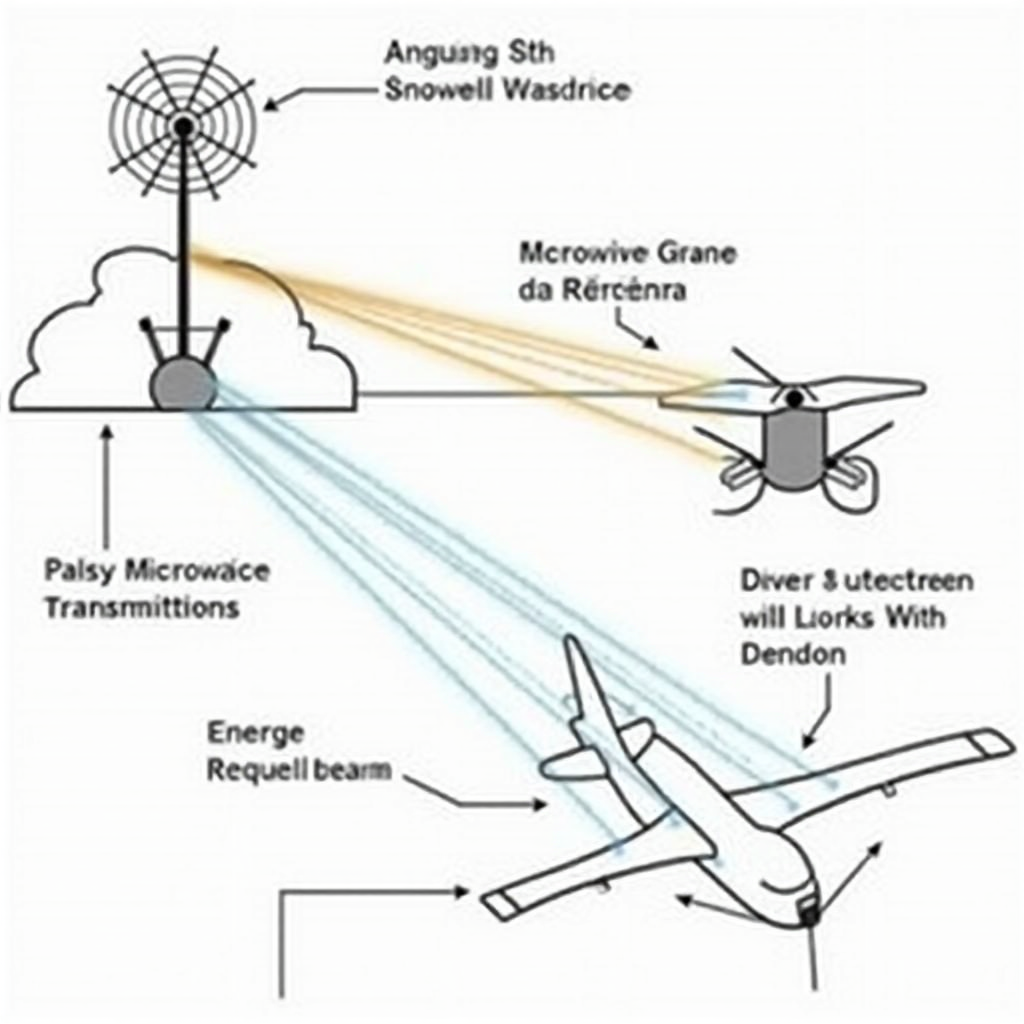
Microwave-powered drones operate on a principle known as wireless power transmission (WPT). Here’s a breakdown of their functioning:
- Microwave Transmission: Ground-based stations emit high-power microwave beams aimed at the drone.
- Energy Reception: The drone is equipped with a special antenna, often a rectifying antenna (rectenna), which captures the microwave energy.
- Power Conversion: The rectenna converts the microwave energy into direct current (DC) electricity.
- Propulsion and Operation: The converted electricity powers the drone’s motors, sensors, and other onboard systems.
- Continuous Power: As long as the drone remains within the microwave beam’s range, it can theoretically remain airborne indefinitely.
Advantages
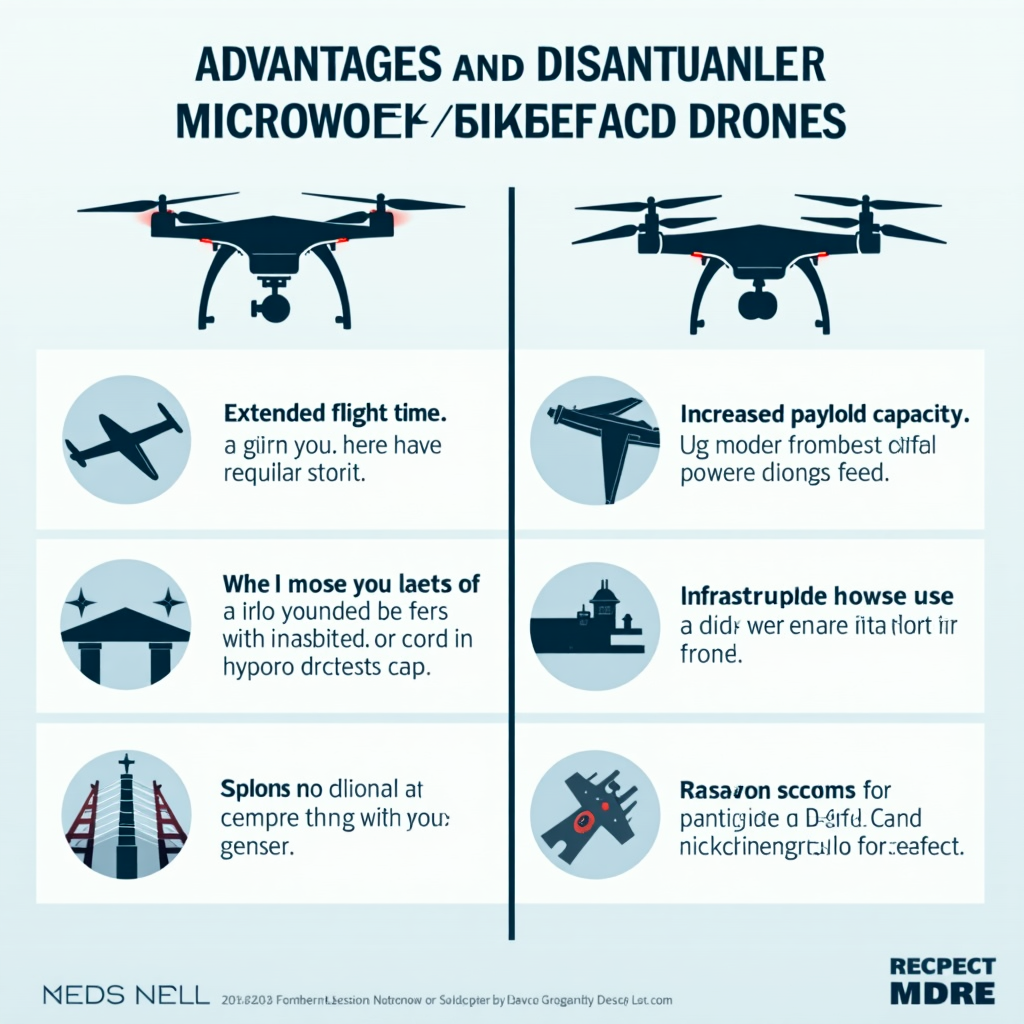
- Extended Flight Time: Unlike battery-powered drones, microwave-powered UAVs can potentially stay airborne for days or even weeks, limited only by mechanical wear.
- Increased Payload Capacity: Without the need for heavy batteries, these drones can carry larger and more diverse payloads.
- Real-time Power Adjustment: Ground stations can modulate power transmission based on the drone’s needs, optimizing energy efficiency.
- Reduced Maintenance: Fewer moving parts and no need for battery replacement lead to lower maintenance requirements.
- Enhanced Range: With strategically placed ground stations, these drones can cover vast areas without landing for recharging.
- Eco-Friendly Operation: Microwave power reduces the reliance on batteries, which often contain harmful materials and have limited lifespans.
Disadvantages
- Infrastructure Requirements: Microwave-powered drones need a network of ground-based power transmission stations, which can be costly to install and maintain.
- Line-of-Sight Limitations: The drone must maintain a clear line of sight with the power transmission station, which can be challenging in urban or mountainous environments.
- Weather Sensitivity: Adverse weather conditions, particularly heavy rain or fog, can interfere with microwave transmission.
- Safety Concerns: High-power microwave beams pose potential health risks, requiring careful management and safety protocols.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The use of high-power microwaves for drone operation faces regulatory challenges in many jurisdictions.
- Vulnerability to Interference: The system could be susceptible to electromagnetic interference, either accidental or intentional (jamming).
Future Scope
The future of microwave-powered drones is promising, with several exciting developments on the horizon:
- Military Applications: Armed forces are exploring these drones for long-endurance reconnaissance missions and as platforms for electronic warfare systems.
- Disaster Response: Their ability to stay airborne for extended periods makes them ideal for coordinating relief efforts in disaster-stricken areas.
- Telecommunications: These drones could serve as mobile, high-altitude communication relays, providing internet and cellular coverage in remote areas.
- Environmental Monitoring: Long-duration flights enable continuous monitoring of large ecosystems, aiding in climate research and wildlife conservation.
- Urban Air Mobility: As technology advances, microwave-powered drones could play a role in future urban transportation systems.
- Space Applications: The technology could be adapted for powering satellites or space-based systems, reducing the need for onboard power generation.
- Advancements in Power Transmission: Ongoing research aims to increase the efficiency and range of wireless power transmission, potentially enabling global drone operations.

