
LAB GROWN MEET
INTRODUCTION
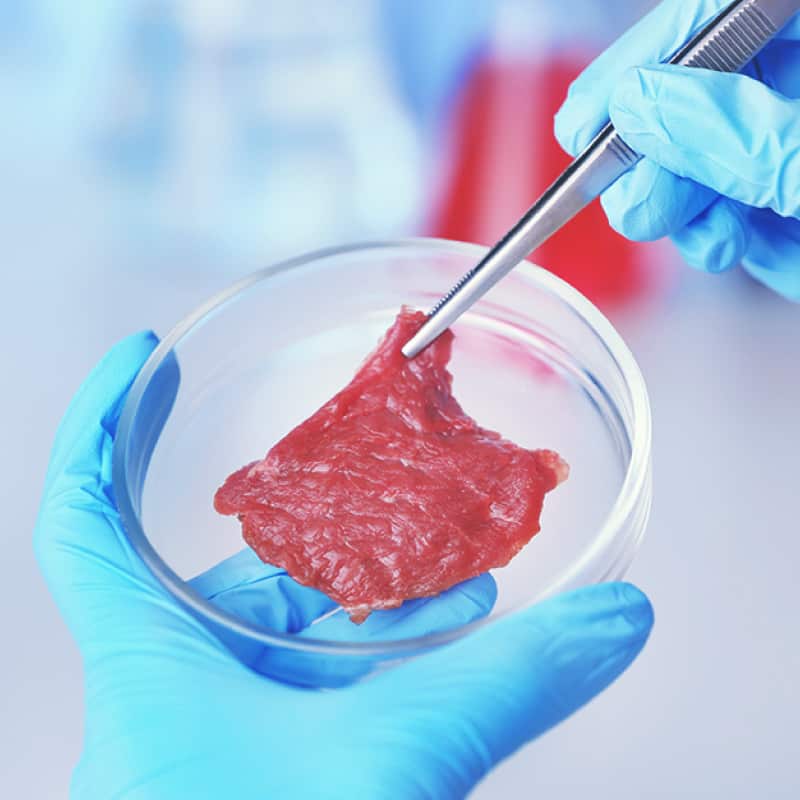
Instead of raising live animals for their meat, to make artificial meat (also known as “slaughter-free meat,” “clean meat” or “cultured meat”), stem cells from an animal’s muscle tissue — known as a donor animal — are combined with a serum. The serum is usually derived from the fetuses of dead cows.
The cells are fed sugar and salts, tricking them into thinking they’re still in an animal — this way they grow.
Over time, the muscle stem cells begin transforming as they strengthen, expand and mature into muscle fibers. Eventually, when enough of these fibers combine, you have a piece of meat.
Fat tissue may then be added to give the meat a flavor more consistent with traditional meat. Then, it’s hello dinner.
Can vegetarians eat lab-grown meat? Because lab-grown meat still requires animal products, it’s not considered vegan or vegetarian-friendly.
TECHNOLOGIES USED IN LAB GROWN MEET
Lab-grown meat, also known as cultivated meat, is produced using cellular agriculture, where animal cells are cultured in a lab to create real meat without the need to raise and slaughter animals. Several advanced technologies are involved in this process, including:
1. Stem Cell Technology
- Scientists extract stem cells (usually muscle satellite cells or pluripotent stem cells) from animals.
- These cells have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into muscle, fat, and other tissue types.
2. Bioreactors (Cultivators)
- Bioreactors (large stainless steel tanks) provide an ideal environment for cells to grow and multiply.
- These devices maintain optimal temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient supply for cell growth.
3. Growth Media (Nutrient Supply)
- Cells need essential nutrients to grow, including:
- Amino acids & proteins (for tissue formation)
- Vitamins & minerals (for cell metabolism)
- Glucose & lipids (for energy)
- Growth factors (to stimulate cell division)
- Initially, fetal bovine serum (FBS) was used, but ethical and cost-effective plant-based alternatives are now being developed.
4. Scaffold Technology
- Scaffolds provide structural support to help cells form the texture and shape of real meat.
- Types of scaffolds include:
- Edible scaffolds (made from soy protein, gelatin, or alginate)
- Biodegradable scaffolds (collagen, mycelium, or nanofiber-based materials)
- 3D-printed scaffolds (used for creating complex meat textures like steak)
5. 3D Bioprinting
- 3D bioprinters use bio-inks made from living cells to print meat structures layer by layer.
- This helps create complex textures, mimicking the muscle fibers in real meat.
6. Tissue Engineering & Cell Differentiation
- Scientists guide stem cells to differentiate into muscle, fat, and connective tissue to mimic the composition of conventional meat.
- Tissue engineering techniques ensure proper cell growth and alignment for better texture.
7. Artificial Intelligence & Automation
- AI and machine learning optimize cell growth conditions, monitor bioreactor environments, and predict the best cell culture parameters for large-scale production.
- Robotics and automation streamline meat cultivation to improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
POTENTIAL BENEFITS
- Results in fewer slaughtered animals — There’d be less need to raise cows if lab meat became more popular, which could potentially cut back on greenhouse emissions.
- Less land and water usage — This would likely follow since fewer cows would need to be raised, and they’d require less food.
- More people can have access to meat — As the world’s population continues growing, farming enough animals to feed meat eaters will take its toll on the planet. Lab meat can be one option for feeding more people animal protein without depleting as many resources. Even today, only about 5 percent of Americans are vegetarian, so there’s big demand for meat. Lab-grown meat, advocates say, provides a solution to the meat scarcity problem and is better for the plant overall.

POTENTIAL DANGERS AND CONCERNS
- Because lab-grown meat is in its infancy, it’s too early to say if the environmental advantages will definitely pan out.
- It’s very expensive to produce.
- The taste is not necessarily appealing to everyone.
- It’s still up for debate how it should be labeled and advertised to consumers.
- It’s not entirely known how healthy is it and how the nutritional content compares real beef and meat.
