EMOTIONAL AI:
Emotional AI, also known as affective computing, is a branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on developing systems capable of recognizing, interpreting, and responding to human emotions by analyzing various cues like facial expressions, voice tone, and body language, essentially allowing machines to understand and react to human feelings in a way similar to how humans do.
Key points about Emotional AI:
- Functionality: It uses advanced technologies like machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing to analyze human emotional states from different inputs like facial expressions, voice intonation, and physiological signals.
- Applications: Emotional AI can be used in various fields including customer service to gauge customer sentiment, healthcare to identify potential mental health issues, education to personalize learning experiences, and even in robotics to create more human-like interactions.
- How it works:
- Facial recognition: Analyzing facial expressions to identify emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, etc.
- Speech analysis: Examining voice pitch, tone, and pace to detect emotional states.
- Physiological sensors: Monitoring physiological responses like heart rate and skin conductance to provide additional emotional insights.
Important aspects to consider:
- Ethical concerns: The potential for misuse of emotional AI, including privacy violations and manipulation of users, raises ethical considerations that need to be addressed.
- Accuracy limitations: While advancements are being made, current emotional AI systems are not perfect and can be influenced by factors like cultural differences and individual variations in emotional expression.
KEY FEATURES:
Emotional AI, also known as affective computing, features the ability to recognize, interpret, and respond to human emotions by analyzing various data points like facial expressions, voice tone, and body language, allowing systems to understand and react to a user’s emotional state, often used in customer service, healthcare, and education to provide more empathetic interactions.
Key features of Emotional AI include:
- Emotion Recognition: The primary function to accurately identify and categorize emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, and fear based on visual cues (facial expressions) and audio cues (voice intonation).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Analyzing text and speech to understand the emotional sentiment expressed within the language.
- Facial Expression Analysis: Detecting subtle facial movements to interpret emotions.
- Voice Analysis: Analyzing pitch, volume, and pace of speech to gauge emotional state.
- Physiological Signal Processing: Integrating data from physiological sensors like heart rate and skin conductance to gain further insights into emotions.
- Contextual Understanding: Taking into account the situation and surrounding factors to interpret emotions more accurately.
- Adaptive Response Generation: Tailoring responses based on the detected emotions, providing empathetic and relevant feedback.
Applications of Emotional AI:
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual assistants with emotional intelligence to understand customer sentiment and provide tailored support.
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient emotions during consultations and treatments, providing mental health support.
- Education: Assessing student engagement and stress levels during learning to adapt teaching methods.
- Marketing and Advertising: Analyzing customer reactions to marketing materials to optimize campaigns.
Ethical Considerations:
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and analyzing emotional data raises privacy issues.
- Bias in Emotion Recognition: AI systems can perpetuate biases present in training data, leading to inaccurate interpretations of emotions across different demographics.
- Misinterpretation of Complex Emotions: Difficulty in accurately identifying nuanced emotions and context-dependent emotional states.

CONS AND PROS OF EMOTIONAL AI:
Emotional AI, while offering potential for enhanced user experiences and personalized interactions, also raises significant concerns regarding privacy, misinterpretation of emotions, and ethical dilemmas, making it crucial to carefully consider both its pros and cons before implementation; pros include improved customer support, potential for early mental health detection, and enhanced user experience through emotional feedback, while cons include privacy violations, difficulty interpreting complex emotions, and potential for manipulation;.
Pros of Emotional AI:
- Improved Customer Support: By understanding customer emotions through facial expressions or voice tone, AI can provide more tailored and empathetic responses, leading to better customer service experiences.
- Enhanced User Experience: Emotional AI can personalize interactions by adapting to the user’s emotional state, creating a more engaging and responsive experience.
- Early Detection of Mental Health Issues: Analysis of speech patterns and facial expressions could potentially flag early signs of mental health concerns.
- Accessibility and Inclusive Design: Emotion AI could potentially improve accessibility for individuals with communication difficulties by interpreting emotional cues beyond spoken words.
- Personalized Learning and Training: Educational platforms can use emotional AI to tailor learning experiences based on a student’s emotional engagement.
Cons of Emotional AI:
- Privacy Concerns: Collecting and analyzing sensitive emotional data raises significant privacy issues, especially when used without informed consent.
- Misinterpretation of Emotions: AI can struggle to accurately interpret complex emotions, leading to potential misjudgments and inappropriate responses.
- Manipulation and Bias: Malicious actors could exploit emotional AI to manipulate users or perpetuate biased decision-making.
- Lack of Emotional Intelligence: While AI can recognize facial expressions, it lacks the nuanced understanding of human emotions and context required for truly empathetic interactions.
- Ethical Dilemmas: Questions arise regarding the use of emotional data in employment decisions, surveillance, and other high-stakes situations.
USES OF EMOTIONAL AI:
Emotional AI, also known as affective computing, is used to analyze and interpret human emotions through facial expressions, voice tone, and body language, allowing systems to respond in a more empathetic and personalized way, with applications in customer service, healthcare, marketing, education, and more; essentially, it helps machines understand and react to human emotions, enabling better interactions across various fields.
Key applications of Emotional AI:
- Customer service: Analyzing customer sentiment in voice and text interactions to identify frustration or satisfaction, allowing customer service agents to tailor their responses accordingly.
- Healthcare: Monitoring patient emotions during consultations or treatments to detect stress or anxiety, providing better support and personalized care.
- Marketing and advertising: Gauging consumer reactions to ads and products by analyzing facial expressions and emotional responses to optimize marketing campaigns.
- Education: Assessing student engagement and emotional state during lessons to adapt teaching methods and identify areas where additional support might be needed.
- Accessibility tools: Assisting individuals with disabilities by interpreting emotions in facial expressions or voice tone, facilitating better communication.
How Emotional AI works:
- Facial expression analysis: Using computer vision to detect facial features and expressions associated with different emotions.
- Voice analysis: Analyzing pitch, tone, and speech patterns to identify emotional states.
- Physiological signals: Monitoring physiological data like heart rate or skin conductance to detect emotional arousal.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP):Analyzing text to identify emotional sentiment and keywords associated with specific emotions.
Potential benefits of Emotional AI:
- Improved user experience: By understanding user emotions, systems can provide more personalized and relevant responses.
- Enhanced customer engagement: Creating more natural and empathetic interactions with customers.
- Early detection of mental health concerns: Identifying potential signs of emotional distress through analysis of speech or facial expressions.
- Data-driven insights: Providing valuable insights into user behavior and emotional responses.
Ethical considerations:
- Privacy concerns: Collecting and analyzing emotional data raises concerns about individual privacy.
- Bias in algorithms: Training data can lead to biased emotion recognition, particularly for underrepresented groups.
- Misinterpretation of emotions: AI systems may not always accurately interpret complex human emotions.

HOW IT WORKS?
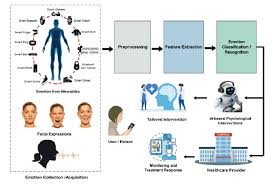
Emotional AI, also known as affective computing, works by utilizing machine learning algorithms to analyze various human cues like facial expressions, voice tone, and body language through computer vision and natural language processing, allowing it to identify and interpret emotional states, then potentially respond in a way that aligns with the detected emotion; essentially, it “reads” human emotions by analyzing visual and auditory data to generate appropriate responses based on the perceived emotional state.
Key points about how emotional AI functions:
- Data collection: Cameras and microphones capture visual and audio data, including facial expressions, eye movements, posture, and voice pitch and tone.
- Feature extraction: Algorithms identify relevant features from the data, such as specific muscle movements on the face or variations in voice pitch, that correspond to emotions.
- Machine learning models: Trained on large datasets of labeled emotional data, these models learn to associate patterns in the features with specific emotions like happiness, sadness, anger, or fear.
- Emotion classification: The AI system analyzes the extracted features and classifies the detected emotion based on the trained model.
- Response generation: Depending on the identified emotion, the AI can then generate a tailored response, such as adjusting its communication style, providing empathetic language, or adapting its behavior to suit the perceived emotional state.
Applications of emotional AI:
- Customer service: Analyzing customer sentiment in voice calls to provide more personalized and empathetic support.
- Healthcare: Detecting emotional distress in patients through facial expressions and voice tone to assist with mental health assessments.
- Education: Monitoring student engagement and emotional responses during learning activities
- Marketing and advertising: Tailoring marketing campaigns based on the emotional response of potential customers
Important considerations:
- Accuracy limitations: While advancements are being made, emotional AI can still misinterpret emotions due to cultural variations, subtle expressions, and complex emotional states.
- Privacy concerns: Collecting and analyzing sensitive emotional data raises privacy issues.
- Ethical implications: Potential for manipulation or biased decision-making based on emotion recognition
REFERENCE:
