DIGITAL TWINS
INTRODUCTION
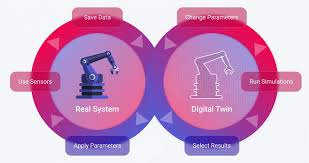
A digital twin is a virtual model of a physical object or system that uses real-time data to simulate its behavior. Digital twins can be used to understand how a physical object works, monitor its performance, and identify potential issues.
How do digital twins work?
- Data sources: Digital twins are linked to real-world data sources, such as sensors on the physical object.
- Real-time updates: The digital twin updates in real time to reflect any changes to the physical object.
- Behavioral insights: Digital twins can include visualizations and insights derived from data.
ADVATAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF DIGITAL TWINS:
Digital twin technology has many advantages, including improved efficiency and decision-making, but it also has some disadvantages.
Advantages
- Predictive maintenance Digital twins can analyze real-time data from equipment and machinery to identify when maintenance is needed. This reduces downtime and saves costs.
- Improved product design Digital twins can visualize manufacturing systems, which helps with product design and collaboration between departments.
- Cost savings Digital twins can help streamline operations and processes, which can lead to cost savings.
- Environmental impact Digital twins can model the impact of climate change and other environmental factors, which can help cities prepare for future challenges.
- Improved quality management Digital twins can process data gathered by IoT devices in real-time, which can help improve quality management.
Disadvantages
- High initial investment: Digital twins can be expensive to implement.
- Complexity: Digital twins can be complex to integrate and maintain.
- Security concerns: Digital twins may be vulnerable to security threats.
- Data quality: Poor data quality can make it difficult to use digital twins effectively.
- Customization requirements: Digital twins may require customization to meet specific needs.
Digital twins are used in many industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, automotive, aerospace, energy, and infrastructure
KEY TRECHNOLOGIES:
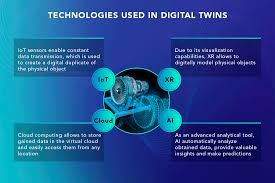
The key technologies used in digital twins are the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Extended Reality (XR), and Cloud.
Internet of Things (IoT)
- IoT devices collect real-time data from physical objects and systems
- IoT sensors measure parameters like temperature, humidity, and vibration
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- AI analyzes data from IoT sensors to understand how physical objects behave
- Machine learning (ML) is an AI technique that creates algorithms to help computer systems perform tasks
Extended Reality (XR)
- Augmented reality (AR) overlays virtual images onto real-world objects
- AR allows users to interact with digital twins more intuitively
Cloud
- Cloud storage and retrieval solutions store and access large amounts of data from IoT sensors
- Cloud storage solutions also offer automation tips
Digital twins are virtual representations of physical objects or processes. They are used to understand and predict the performance of the physical counterpart.
Digital twins can help with:
- Improving production efficiency
- Conserving resources like water and energy
- Reducing pollution and waste
- Improving supply chain traceability
- Reducing environmental waste
- Optimizing energy management
- Reducing carbon emissions
USES OF DIGITAL TWIN:
Digital twins are primarily used to create virtual replicas of physical assets or processes, allowing for real-time monitoring, analysis, and optimization by simulating various scenarios, which is particularly valuable in manufacturing, automotive, construction, and healthcare industries for tasks like predictive maintenance, design improvement, performance optimization, and identifying potential issues before they occur in the real world; essentially enabling better decision-making through data-driven insights.
Key applications of digital twins include:
- Manufacturing: Identifying potential equipment failures through predictive maintenance, optimizing production processes, and improving product quality by simulating design changes before physical production.
- Automotive: Simulating vehicle performance under different conditions, optimizing design during development, and identifying potential issues in production lines.
- Construction: Monitoring building performance in real-time, optimizing energy efficiency, and identifying potential design flaws before construction begins.
- Healthcare: Analyzing patient data to predict potential health risks, developing personalized treatment plans, and simulating surgical procedures.
- Energy Management :Optimizing energy grid operations, predicting energy consumption patterns, and improving efficiency of renewable energy sources like wind turbines.
- Supply Chain Management: Identifying bottlenecks in logistics, optimizing inventory levels, and simulating different delivery scenarios.
- Asset Management: Monitoring the health of critical assets, scheduling preventative maintenance, and maximizing asset lifespan.
Key benefits of using digital twins:
- Improved efficiency: By identifying areas for optimization and proactively addressing potential issues.
- Cost reduction: Minimizing downtime, preventing costly failures, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced decision making: Providing real-time data and insights to support informed decisions.
- Innovation acceleration: Enabling rapid prototyping and testing of new designs and concepts.
REFERENCE:

