BIO DEGRADABLE ELECTRONICS
INTRODUCTION

Biodegradable electronics are electronic devices designed to decompose naturally when they are no longer in use.
Unlike conventional electronics, which can take hundreds of years to break down, Bio-based electronics are made from materials that can be broken down by natural processes into harmless substances.
These materials include organic polymers, cellulose, and even proteins, which are environmentally friendly and non-toxic.
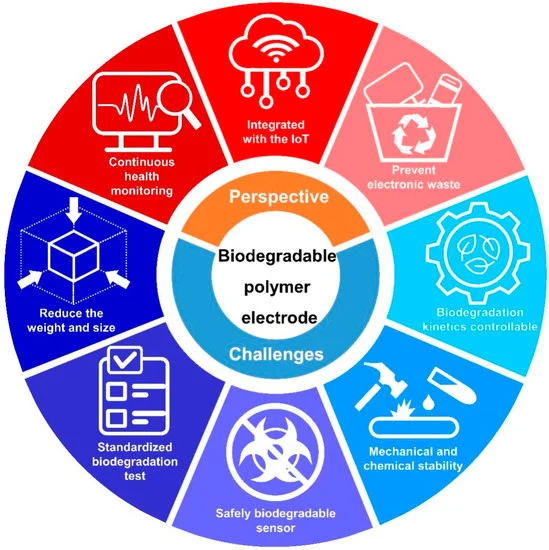
WORKING OF BIODEGRADABLE ELECTRONICS
Biodegradable devices function by utilizing materials that break down gradually when exposed to natural environmental factors like moisture, sunlight, and microbial processes. For example, researchers have developed biodegradable circuit boards using cellulose nanofibers and conductive inks made from organic materials. When these devices are discarded, they can break down into non-toxic components, significantly reducing the environmental impact.
KEY COMPONENTS:
Biodegradable Substrates: These are the basic materials used to build electronic components. Common biodegradable substrates include cellulose, silk protein, and various polymers derived from natural sources.
Conductive Materials: Traditional metals used in electronics are not biodegradable. Researchers are exploring the use of organic materials like carbon nanotubes and conductive polymers that can decompose without leaving toxic residues.
Degradable Semiconductors: Semiconductors are essential for electronic functionality. Biodegradable alternatives, such as those made from zinc oxide and magnesium, are being developed to replace conventional materials.

POTENTIAL BENEFITS OF BIODEGRADABLE ELECTRONICS:
Reducing Environmental Pollution
Traditional electronics contribute significantly to pollution due to their non-biodegradable components. When these devices are discarded, they can release toxic substances into the environment. On the other hand, biodegradable gadgets decompose naturally, minimizing the release of harmful chemicals and reducing pollution.
Minimizing Health Risks – E-waste contains hazardous materials that can pose serious health risks to humans. For example, exposure to lead and mercury can cause neurological damage and other health problems. By using biodegradable materials, the risk of exposure to these toxic substances is significantly lowered, promoting a healthier environment.
Encouraging Sustainable Manufacturing—The development of biodegradable electronics encourages manufacturers to adopt more sustainable practices. These include using renewable resources, reducing energy consumption, and minimizing waste during production. As a result, the entire lifecycle of electronic devices becomes more environmentally friendly.
Promoting Circular Economy- A circular economy‘s main motto is to keep resources in use for as long as possible, extracting maximum value before recovering and regenerating materials. Bio-based electronics fit perfectly into this model. After their useful life, these devices can decompose and return to the earth, where they can contribute to the growth of new raw materials, creating a continuous cycle of sustainability.
CHALLENGES OF BIODEGRADABLE ELECTRONICS: