Introduction
Synthetic meat, also known as lab-grown meat or cultured meat, is produced by cultivating animal cells in a laboratory, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional meat production. This innovative method involves taking a small sample of animal cells, growing them in a nutrient-rich environment, and allowing them to multiply into muscle tissue. The result is real meat without the need to raise and slaughter animals. As the world faces environmental, ethical, and food security challenges, lab-grown meat could revolutionize the food industry by addressing many of the problems associated with conventional meat production.
How It Works
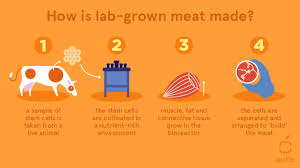
Lab-grown meat production begins with harvesting a small sample of animal cells, typically muscle cells, from a live animal. These cells are then placed in a bioreactor, where they are provided with the necessary nutrients, such as sugars, amino acids, and growth factors, to grow and replicate. Over time, the cells multiply and differentiate into muscle fibers, mimicking the texture and structure of conventional meat. The process can take weeks or months, depending on the type of meat being cultivated. Once grown, the tissue is harvested, processed, and prepared for consumption.
Potential Benefits
- Environmental Sustainability:
Traditional meat production is a major contributor to deforestation, greenhouse gas emissions, and water consumption. Lab-grown meat could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of meat production by eliminating the need for large-scale animal farming and land use. It also reduces methane emissions associated with livestock. - Ethical Considerations:
Lab-grown meat offers a more humane alternative to conventional meat production, as it eliminates the need for animal slaughter. This could appeal to consumers who are concerned about the ethical implications of eating animals but still desire the taste and nutritional benefits of meat. - Food Security:
With the global population expected to reach 9 billion by 2050, the demand for food will increase significantly. Lab-grown meat could provide a sustainable and scalable solution to meet the growing need for protein, especially in areas where traditional farming may be less feasible due to climate change or resource limitations. - Health Benefits:
Lab-grown meat can be engineered to have healthier nutritional profiles, such as lower fat content or the inclusion of additional nutrients. This could help address concerns about the high levels of saturated fat and cholesterol found in conventional meat, offering a healthier alternative. - Reduced Risk of Disease:
Traditional meat production is often associated with the spread of diseases such as mad cow disease and avian influenza. Since lab-grown meat is produced in sterile, controlled environments, it eliminates the risk of zoonotic diseases (diseases that jump from animals to humans).
Why It’s Underrated

Despite its potential to revolutionize the food industry, lab-grown meat remains relatively underrated for several reasons:
- High Costs: The production of lab-grown meat is still expensive, with costs per kilogram remaining high due to the complexity of the process and the need for specialized equipment. However, costs are expected to decrease as technology advances and economies of scale are achieved.
- Public Perception: Many consumers remain skeptical about the idea of eating meat that has been grown in a lab, associating it with science fiction or concerns over food safety. Overcoming these perceptions will be crucial for widespread adoption.
- Regulatory Challenges: Lab-grown meat is still subject to strict regulations in many countries, and it may take years for it to be widely approved for sale in certain markets. There are also concerns over labeling and ensuring the safety of lab-grown meat for human consumption.
Challenges Ahead
- Scaling Production:
Although lab-grown meat has shown promise in small-scale production, scaling up to meet global demand will require significant technological advancements and investment. Efficient bioreactors, better cell lines, and cost-effective production methods are essential for making lab-grown meat viable on a large scale. - Consumer Acceptance:
Many people are hesitant to adopt lab-grown meat due to concerns over its taste, texture, and safety. Educating consumers about the benefits and safety of lab-grown meat will be key to its success in the market. - Regulatory Hurdles:
Governments and food safety agencies need to develop clear regulations for the production and sale of lab-grown meat. The process of gaining regulatory approval could be slow and costly, delaying the widespread availability of cultured meat.
Conclusion
Lab-grown meat offers a promising solution to the environmental, ethical, and food security challenges posed by traditional meat production. By eliminating the need for animal farming and slaughter, it could significantly reduce the environmental impact of meat production while providing a sustainable source of protein for the future. While the technology is still in its infancy, with challenges related to cost, consumer perception, and regulatory approval, lab-grown meat has the potential to transform the global food system. As technology advances and public acceptance grows, cultured meat could become a mainstream part of our diets, paving the way for a more sustainable and ethical food industry.

