
FOOD WASTE REDUCTION SYSTEM

INTRODUCTION
Food waste is a major global issue, with millions of tons of edible food discarded each year.
This waste occurs at various stages of the supply chain, from production and transportation to retail and consumer levels.
Reducing food waste is essential for addressing hunger, environmental sustainability, and economic efficiency.
By implementing strategies such as better storage, mindful consumption, improved supply chain management, and innovative food recovery solutions, individuals, businesses, and governments can work together to minimize food waste.
Cutting down on waste not only conserves resources like water and energy but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, making it a crucial step toward a more sustainable and food-secure future.

TECHNOLOGIES USED IN FOOD WASTE REDUCTION
- Technologies like precision agriculture systems, IoT-enabled storage sensors, and smart harvesting equipment can help minimize waste during critical stages of production and storage. Implementing sustainable food waste management practices is equally essential.

WORKING OF FOOD WASTE REDUCTION
Prevention (Minimizing Waste at the Source)
- Efficient Farming Practices – Optimizing harvesting, reducing crop losses, and improving supply chain coordination.
- Better Inventory Management – Businesses use AI and tracking systems to order only what is needed.
- Consumer Awareness – Educating people about portion control, meal planning, and proper food storage.
- Smart Packaging – Technologies like freshness sensors and vacuum-sealed packaging extend shelf life.
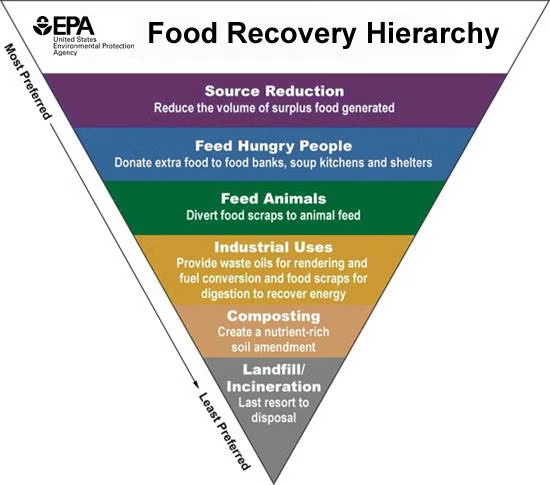
2. Redistribution (Reusing Edible Surplus Food)
- Food Recovery Programs – Surplus food from restaurants, supermarkets, and events is donated to food banks or shelters.
- Ugly Produce Campaigns – Selling imperfect but edible fruits and vegetables at lower prices to reduce waste.
3. Repurposing (Using Leftover or Surplus Food)
- Creative Cooking – Restaurants and households use leftovers creatively to reduce waste.
- Byproduct Utilization – Using food waste in new ways, such as making soups, sauces, or animal feed.
4. Recycling (Converting Waste into Useful Products)
- Composting – Organic food waste is turned into nutrient-rich compost for farming.
- Bioenergy Production – Food scraps are processed in anaerobic digesters to produce biogas and electricity.
- Upcycling Food Waste – Converting waste into new food products, like making flour from fruit peels or snacks from surplus grains.
5. Policy & Technology Support
- Government Regulations – Policies to limit food waste in industries and promote donation incentives.
- Food Tracking & AI – Smart apps and AI systems help businesses and consumers track expiration dates and reduce waste.

PROS AND CONS:
Pros (Advantages)
- Environmental Benefits 🌍
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing food in landfills.
- Lowers water and energy consumption used in food production.
- Economic Savings 💰
- Households and businesses save money by buying and using only what they need.
- Reduces costs for waste management and landfill operations.
- Food Security & Hunger Reduction 🍽️
- Surplus food can be redistributed to food banks and shelters to help those in need.
- Maximizing food use ensures better availability for growing populations.
- Sustainable Agriculture 🌱
- Reduces the demand for excessive farming, which helps preserve natural resources.
- Encourages responsible food production and consumption habits.
- Innovations in Waste Management ⚙️
- Advances in composting, biogas production, and food upcycling create new business opportunities.
- Encourages the development of AI and smart technologies for tracking and reducing waste.
❌ Cons (Challenges & Drawbacks)
- High Initial Costs for Businesses 💵
- Implementing food waste tracking systems, new packaging, and redistribution programs can be costly.
- Consumer Behavior & Awareness Issues 🤷
- Many people are unaware of proper food storage, portion control, and expiration label meanings.
- Changing long-standing food habits takes time and effort.
- Logistics Challenges 🚛
- Collecting and distributing surplus food requires proper storage, transportation, and coordination.
- Perishable foods must be handled quickly to avoid spoilage.
- Limited Infrastructure for Recycling & Composting 🏗️
- Not all areas have accessible composting or food waste recycling programs.
- Some businesses lack incentives or facilities for sustainable waste disposal.
- Legal & Regulatory Barriers ⚖️
- Strict food safety laws can prevent businesses from donating surplus food.
- Expiration date confusion leads to unnecessary disposal of still-edible food.

