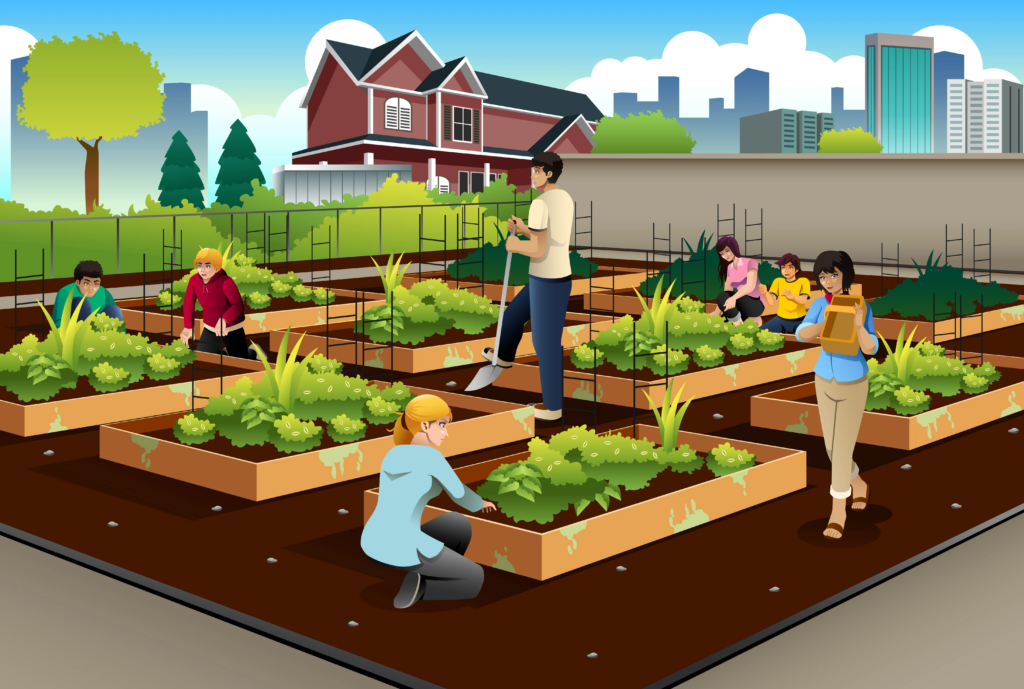
URBAN FORMING:
Urban farming, also known as urban agriculture, is the practice of cultivating crops and raising livestock within the boundaries of a city, utilizing various spaces like rooftops, vacant lots, balconies, and community gardens to produce food for local consumption, often employing innovative techniques to maximize space and sustainability in an urban environment; it aims to increase access to fresh produce, promote community engagement with agriculture, and contribute to environmental benefits by reducing food transportation distances and carbon footprint.
Key points about urban farming:
- Diverse practices:Includes rooftop gardens, vertical farming, hydroponics, aquaponics, community gardens, backyard plots, and even raising small livestock depending on local regulations.
- Benefits:
- Food security: Provides fresh, locally grown food, improving access to nutritious produce, especially in food deserts.
- Environmental impact: Reduces carbon emissions from food transportation, improves air quality by increasing green spaces, and can utilize recycled water.
- Community building: Fosters social interaction and connection through shared gardening activities.
- Economic opportunities: Creates jobs and supports local economies through the production and sale of fresh produce.
- Challenges:
- Limited space: Efficiently utilizing small areas is crucial.
- Regulations: Navigating zoning laws and permitting processes for urban farming
- Access to resources: Ensuring adequate water supply, soil quality, and technical expertise

KEY TECHNOLOGIES:
Urban farming uses a variety of technologies, including hydroponics, aquaponics, vertical farms, aeroponics, green roofs, and farm automation.
Hydroponics and aquaponics
- Hydroponics: A soil-less farming technique that uses water to grow plants
- Aquaponics: A combination of hydroponics and fish farming, where fish waste fertilizes plants
Vertical farms
- Use up to 70% less water than traditional farms
- Can be used to grow crops in controlled environments
- Can be automated to customize environmental conditions
Aeroponics
- A type of hydroponic system that sprays nutrients on roots as a mist instead of submerging them in water
Green roofs
- Reduce urban heat islands, improve air quality, and absorb stormwater
Farm automation
- Uses sensors to monitor and control environmental conditions
- Can be used to customize conditions for functional foods
Artificial intelligence
- Can be used to control environments in vertical farms
Community gardens
- A farming model that can help address food security in cities
Urban farming can help address food security in cities.

ADVANTAGES AND CHALLENGES OF URBAN FARMING:
Urban farming can have many advantages, including environmental, economic, and social benefits. However, it also faces challenges like limited space and soil contamination.
Advantages
- Environmental benefits: Urban farming can improve air quality, regulate the climate, and create habitats for pollinators and birds.
- Economic benefits: Urban farming can help reduce food insecurity and save money on groceries.
- Social benefits: Urban farming can help build community cohesion and engagement.
- Food safety: Food grown close to consumers stays fresher longer, which can reduce food waste.
- Health benefits: Urban farming can provide access to fresh, healthy food that is pesticide-free.
Challenges
- Limited space: Urban farming can face challenges due to limited space.
- Soil contamination: Urban farming can face challenges due to soil contamination.
- Limited access to resources: Urban farming can face challenges due to limited access to water and other resources.
- Regulatory barriers: Urban farming can face challenges due to regulatory barriers.
To address these challenges, policymakers, urban planners, and community organizations can work together.

USES:
Urban farming can help with food security, community engagement, and economic opportunities. It can also help reduce carbon footprint and save space.
Food security
- Urban farming can help ensure that people have enough access to fresh fruits and vegetables
- It can help people move from unhealthy diets to healthier lifestyles
Community engagement
- Urban farming can help create social connections and educate people about agriculture
- Community gardens and rooftop farms can unite people
Economic opportunities
- Urban farming can help provide job training and opportunities for youth
- It can help empower people who are unemployed, underemployed, or malnourished
Conserve space
- Vertical farming can save space by growing crops in stacked layers
- It can reduce carbon footprint by bringing food production closer to consumers
Technology
- Urban farming uses technologies like hydroponics and aquaponics to grow plants without soil or with fish waste
- These technologies can help control nutrients, pH level, and water usage
- They can also help produce leafy greens and herbs using minimal water and energy
HOW IT WORKS?
Urban farming involves growing food crops, fruits, vegetables, and sometimes even livestock within urban areas, utilizing limited spaces like rooftops, vacant lots, and even vertical structures by employing innovative techniques like hydroponics, aquaponics, and vertical farming to maximize production and ensure fresh, locally-sourced food for city dwellers; essentially, it’s about cultivating food in a city environment by optimizing space and using advanced methods to produce a variety of crops, often with community involvement and a focus on sustainability.
Key aspects of urban farming:
- Space utilization: Urban farms make use of underutilized spaces like rooftops, abandoned lots, walls, and even unused parking areas to grow crops vertically or in raised beds, maximizing production in limited space.
- Innovative techniques:
- Hydroponics: Growing plants in nutrient-rich water without soil, reducing water usage.
- Aquaponics: Integrating fish farming with hydroponics, where fish waste provides nutrients for plants and the plants clean the water for the fish.
- Vertical farming: Stacking plants on multiple levels to maximize growing space within a smaller footprint.
- Community involvement: Many urban farms are community-based, allowing residents to participate in growing their own food, fostering social connection and education about sustainable practices.
- Local food production: By growing food within the city, urban farming reduces the need for long-distance transportation, promoting fresher produce and minimizing carbon footprint.
Examples of urban farming practices:
- Rooftop gardens: Growing vegetables and herbs on rooftops of buildings
- Community gardens: Shared plots where residents can cultivate food together
- Vertical farms: Multi-tiered growing systems in controlled environments, often indoors
- Container gardening: Utilizing large containers to grow plants on balconies or patios
- Urban beekeeping: Raising honeybees in urban areas to pollinate plants
Benefits of urban farming:
- Improved food security: Provides access to fresh, local produce for city residents
- Environmental benefits: Reduces carbon emissions from food transportation, promotes biodiversity
- Economic opportunities: Creates jobs and supports local businesses
- Community building: Encourages social interaction and education about sustainable practices


