Introduction
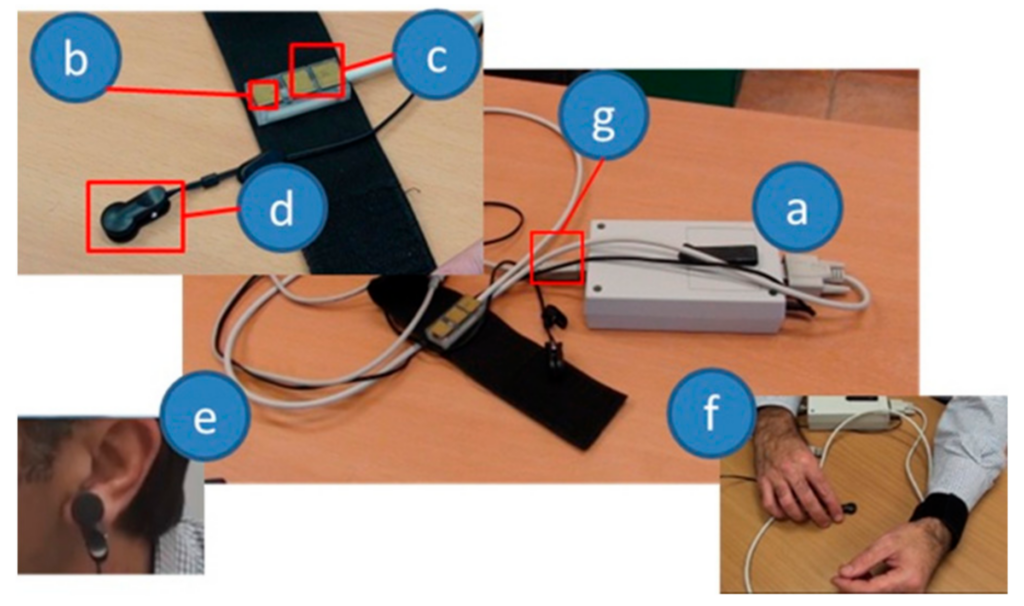
In the high-stakes environment of modern warfare, soldiers are exposed to extreme stressors that can significantly impact their performance, mental health, and decision-making abilities. As military operations become more complex and challenging, managing stress effectively has become a priority. Biofeedback devices have emerged as a promising solution to help soldiers manage stress in real-time, improving their performance while enhancing their overall well-being.
Biofeedback devices are wearable or sensor-based technologies that provide soldiers with real-time information about their physiological states, enabling them to monitor and control their stress responses. By leveraging these devices, soldiers can learn to regulate their stress levels and enhance focus, ultimately leading to improved mental resilience and better operational effectiveness.
This article explores how biofeedback devices work, the technology behind them, their uses, advantages, and disadvantages in military applications.
How Biofeedback Devices Work in Soldier Stress Management
Biofeedback devices function by providing real-time data about an individual’s physiological functions—such as heart rate, blood pressure, skin conductivity, respiration, and brain activity—to help individuals understand their stress responses. The core principle is based on the idea that by becoming aware of how their body reacts to stress, individuals can consciously learn to control these reactions.
The process works as follows:
- Sensors: Biofeedback devices use various sensors that measure physiological responses. These sensors are usually attached to the skin, head, or fingers, depending on what aspect of stress or physiology is being monitored. For example:
- Heart rate sensors measure the heart rate and heart rate variability (HRV), which can indicate stress or relaxation.
- Electrodermal activity (EDA) sensors monitor skin conductivity, which can be an indicator of stress.
- EEG sensors can track brainwave activity, providing insight into the soldier’s mental state.
- Real-Time Data Display: The sensors transmit the collected data to a display unit (either through a mobile app or integrated into a wearable device like a wristband or headband). The soldier can see immediate feedback on their physiological states.
- Training and Control: By receiving real-time feedback, soldiers can practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, relaxation exercises, or cognitive control. The idea is that through continued practice, soldiers can learn to control their physiological responses to stress, promoting mental clarity, focus, and emotional stability.
- Wearable Devices: Many modern biofeedback devices are compact and wearable, making them ideal for military personnel. They can be worn on the wrist, head, or chest, allowing soldiers to use them in both training and combat environments. These devices can be integrated into uniforms or equipment without being cumbersome.
Technology Behind Biofeedback Devices for Soldier Stress Management
Biofeedback devices leverage cutting-edge sensor technologies, signal processing, and data analytics to provide soldiers with real-time insight into their physiological states. Some of the key technological components include:
- Wearable Sensors: These sensors monitor and measure various physiological signals such as heart rate, skin conductivity, body temperature, and muscle tension. Some advanced sensors can also monitor brainwave activity through EEG (electroencephalography), providing insight into the soldier’s mental state.
- Wireless Communication: Many biofeedback devices use wireless technologies such as Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to transmit data to a mobile device or central unit. This enables real-time monitoring of soldiers’ stress levels during both training and combat situations.
- Data Analytics and Feedback Systems: Advanced data processing algorithms analyze the physiological data collected by the sensors. The feedback system then presents actionable insights, such as visual cues (graphs, charts) or auditory signals (beeps, tones) that alert soldiers to changes in their stress levels. Some systems may also provide suggestions for managing stress based on the data analysis.
- Cloud Integration: Some biofeedback devices are connected to cloud platforms, allowing for long-term tracking of soldiers’ stress patterns, performance metrics, and health conditions. This data can be used by military healthcare professionals to assess the soldier’s readiness and well-being over time.
Uses of Biofeedback Devices in Soldier Stress Management
Biofeedback devices serve several important functions when it comes to managing soldier stress, including:
- Stress Awareness and Monitoring:
- Biofeedback devices provide soldiers with real-time awareness of their physiological responses to stress. This helps them understand when their stress levels are becoming elevated and take corrective action before it impairs their performance.
- Performance Enhancement:
- By learning to control their physiological responses, soldiers can maintain optimal focus and decision-making abilities under pressure. Biofeedback devices can improve cognitive performance, reaction time, and overall mental clarity, which are essential in combat situations.
- Mental Resilience Training:
- Soldiers can use biofeedback devices as part of mental resilience and stress inoculation training. These devices can help soldiers practice relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, to reduce physiological stress markers and improve their ability to stay calm in high-stress situations.
- Recovery and Recovery Monitoring:
- Biofeedback devices can help soldiers monitor how well they are recovering after high-stress events or combat. By tracking physiological recovery, soldiers and medical personnel can ensure that soldiers are not overexerting themselves and are returning to baseline health before engaging in further activities.
- Mental Health Support:
- Biofeedback devices can be used in conjunction with mental health programs to track symptoms of anxiety, PTSD, and other stress-related disorders. Early detection of stress and mental health issues through biofeedback allows for timely intervention and support.
Advantages of Biofeedback Devices for Soldier Stress Management
- Real-Time Stress Management:
- Biofeedback devices provide instantaneous feedback on a soldier’s physiological state, enabling them to take immediate action to manage their stress levels. This immediate awareness can help prevent stress from affecting decision-making and operational performance.
- Improved Cognitive and Physical Performance:
- Soldiers who can effectively manage their stress levels using biofeedback devices experience improved focus, cognitive function, and physical endurance. This leads to better decision-making under pressure, which is critical in high-risk environments.
- Mental Resilience and Training:
- Continuous use of biofeedback devices can help soldiers develop mental resilience and coping mechanisms, ensuring they are better prepared to handle the psychological demands of combat and stressful situations.
- Portable and Non-Invasive:
- Biofeedback devices are typically non-invasive and easy to use, making them well-suited for deployment in the field. Wearable devices like wristbands or headbands are lightweight and can be used without disrupting the soldier’s daily activities.
- Personalized Stress Management:
- Each soldier’s stress responses are unique, and biofeedback devices offer personalized feedback to help them manage their specific stress triggers. This tailored approach helps maximize the effectiveness of stress management techniques.
Disadvantages of Biofeedback Devices for Soldier Stress Management
- Dependence on Technology:
- There is a risk that soldiers may become overly reliant on biofeedback devices, possibly leading to reduced self-awareness and resilience if the devices are unavailable or malfunction during critical situations.
- Training and Adaptation Period:
- Although biofeedback devices can provide instant feedback, soldiers may require a significant training period to learn how to use the devices effectively. The learning curve could be a barrier, especially in high-pressure environments.
- Privacy Concerns:
- Since biofeedback devices collect sensitive physiological data, there may be concerns regarding the privacy and security of the data. The potential for this data to be misused or mishandled needs to be addressed.
- Limited Effectiveness in Severe Stress:
- While biofeedback is effective for managing low to moderate stress, it may be less effective for soldiers experiencing severe trauma or acute stress reactions. In such cases, traditional mental health support or intervention may still be necessary.
- Maintenance and Calibration:
- Biofeedback devices require regular maintenance and calibration to ensure accurate readings. If devices are not properly maintained, the data they provide may be unreliable, reducing their effectiveness in stress management.
Conclusion
Biofeedback devices represent a powerful tool for managing stress and enhancing soldier performance, offering real-time physiological data and enabling soldiers to gain greater control over their mental and emotional states. By incorporating biofeedback into military training and operational strategies, armed forces can enhance the resilience, focus, and decision-making capabilities of their personnel in high-pressure environments.
However, there are challenges and limitations to the technology, such as dependence on devices and privacy concerns. As biofeedback technology continues to evolve, further advancements and refinements will likely address these challenges, making biofeedback a staple in military mental health and stress management programs for the future.
