
Introduction:
Smart highways represent the next frontier in transportation technology, designed to improve traffic flow, enhance road safety, and provide a more sustainable and efficient driving experience. These highways are equipped with advanced technologies that collect, process, and analyze data in real-time to create a smarter and more responsive infrastructure. By leveraging Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, and artificial intelligence (AI), smart highways aim to optimize traffic patterns, reduce congestion, and minimize environmental impact. As urban populations grow and transportation demands increase, smart highways are being seen as a vital solution to address the challenges of modern mobility.
How It Works:
Smart highways incorporate a range of technologies that enable them to function effectively. Here’s an overview of how these highways work:
- Sensors and Cameras: Smart highways are equipped with sensors embedded in the road surface, roadside cameras, and other monitoring systems to gather real-time data on traffic flow, road conditions, and vehicle speeds. This data is transmitted to central systems for analysis and decision-making.
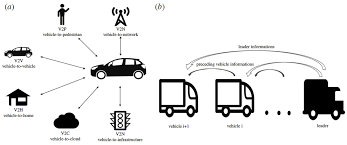
- Communication Systems: The collected data is sent to communication networks, allowing vehicles to interact with infrastructure in real time. This allows for the dissemination of traffic updates, road conditions, accidents, and other relevant information to drivers through various channels, such as roadside displays or connected car systems.
- Adaptive Traffic Management: Based on the real-time data received, smart highways can adjust traffic signals, lane assignments, and speed limits to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion. These systems can dynamically respond to traffic conditions, such as heavy traffic, accidents, or weather changes, ensuring smoother driving experiences.
- Intelligent Lighting: Smart lighting systems adjust the brightness of streetlights based on traffic presence, weather conditions, or time of day. For example, lights may be dimmed during low-traffic hours or when no vehicles are detected in certain areas, conserving energy.
- Electric Vehicle Charging: Some smart highways integrate infrastructure for electric vehicle (EV) charging. These highways feature strategically placed charging stations that can be accessed by EVs while on the road, helping to promote the adoption of clean energy vehicles.
Technology Used:
Several advanced technologies are employed in the development and operation of smart highways:
- IoT (Internet of Things): IoT devices, such as sensors, cameras, and smart traffic signals, play a critical role in collecting and transmitting data. These devices allow smart highways to interact with vehicles and infrastructure in real-time.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI algorithms analyze the vast amounts of data collected from the sensors and cameras. Machine learning models can predict traffic patterns, detect accidents or hazards, and recommend solutions for optimizing traffic flow.
- Connected Vehicles: With the rise of autonomous and connected vehicles, smart highways can communicate directly with vehicles to provide route updates, inform drivers of road conditions, and even adjust the driving experience based on real-time traffic data.
- Big Data Analytics: The data collected from smart highways is processed and analyzed through big data platforms. These platforms can provide valuable insights into traffic behavior, patterns, and trends, helping urban planners improve infrastructure and reduce congestion.
- Electric Vehicle Infrastructure: Smart highways are integrating EV charging stations equipped with advanced power management systems. These charging stations are designed to provide fast and efficient charging, often powered by renewable energy sources.
- Dynamic Roadways: Some smart highways feature dynamic roadways, such as lanes that change direction based on traffic demand, or roads that can heat up to melt snow and ice during cold weather conditions.
Advantages:
- Improved Traffic Flow: Real-time monitoring and adaptive traffic management reduce congestion, making travel more efficient and reducing travel time.
- Enhanced Road Safety: Smart highways can detect accidents or dangerous conditions and immediately send alerts to drivers, enabling them to make safer decisions. Features like lane departure warnings and automatic speed adjustments further enhance safety.
- Environmental Sustainability: By reducing traffic congestion and optimizing traffic flow, smart highways can decrease emissions and fuel consumption. Additionally, the integration of EV charging stations encourages the adoption of electric vehicles, further reducing the carbon footprint.
- Cost Savings: The ability to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion can result in significant cost savings for both individuals and municipalities. These savings come from reduced fuel consumption, fewer accidents, and less wear and tear on vehicles.
- Energy Efficiency: The use of intelligent street lighting systems helps conserve energy by adjusting brightness based on traffic and weather conditions. Additionally, electric vehicle charging infrastructure promotes the use of clean energy.
- Support for Autonomous Vehicles: Smart highways are designed to support the operation of autonomous vehicles by providing real-time data, communication infrastructure, and intelligent traffic management systems.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Costs: Building and maintaining smart highways requires significant financial investment. The installation of sensors, cameras, communication systems, and the development of the necessary infrastructure can be expensive for governments and private entities.
- Privacy Concerns: The widespread use of sensors and cameras to monitor traffic could raise privacy concerns among individuals, as it may involve the collection of personal data without consent. The potential for surveillance and data misuse must be addressed.
- Vulnerability to Cyberattacks: The connected nature of smart highways makes them susceptible to cyberattacks. Hackers could potentially disrupt traffic management systems, manipulate data, or disable infrastructure, posing significant risks to public safety.
- Technological Inequality: The implementation of smart highways may not be equally distributed, with rural or less developed areas potentially lacking access to these advanced technologies. This could lead to a digital divide in terms of transportation infrastructure.
- Maintenance Challenges: With the use of advanced technologies, the maintenance and repair of smart highways become more complex. Ensuring that the systems are regularly updated and functioning optimally is essential, but can be resource-intensive.
Future Scope:
The future of smart highways is full of potential as technological advancements continue to shape the way we travel:
- Widespread Adoption: As the benefits of smart highways become more evident, we can expect broader adoption worldwide. Governments and cities are likely to invest in the development of smart highways as part of their urban planning initiatives, particularly as more regions move toward sustainable and connected transportation systems.
- Integration with Smart Cities: Smart highways will become an integral part of the larger smart city ecosystem. As cities adopt more intelligent infrastructure, smart highways will be linked to broader systems for energy management, waste management, public services, and more.
- Improved Autonomous Vehicle Integration: With the continued growth of autonomous vehicles, smart highways will evolve to provide better integration with these vehicles. Vehicle-to-infrastructure communication will allow for seamless driving experiences, improving both safety and efficiency.
- Sustainability Focus: Future smart highways may feature more green initiatives, such as the use of renewable energy sources to power charging stations, intelligent energy grids, and sustainable construction materials.
- Advanced AI and Data Analytics: As AI and big data technologies advance, smart highways will become even more intelligent. These systems will predict traffic behavior, manage congestion more efficiently, and reduce the impact of accidents or incidents on roadways.
- Global Expansion: As smart highway technologies mature, countries around the world will look to integrate these systems into their transportation infrastructure. This could significantly reduce the environmental impact of transportation, improve road safety, and reduce urban congestion.
