BIOMIMICRY
INTRODUCTION:
Biomimicry is a design approach that uses nature’s strategies to solve human challenges. It is based on the idea that nature has already tested and found solutions that work best. The goal of biomimicry is to create sustainable products, processes, and systems.
How does biomimicry work?
- Learn from nature: Observe how living organisms solve problems.
- Emulate nature: Use what you’ve learned to create designs that are more efficient, resilient, and sustainable.
- Consider the impact: Make sure your designs are ethical and help conserve and protect nature.
Examples of biomimicry
- Solar cells that mimic tree leaves
- Antibacterial paints that mimic sharkskin
- Businesses that improve their organizational structures based on redwood groves
- Hingeless shading systems inspired by the bird-of-paradise flower
How can I introduce biomimicry?
- Define the word biomimicry
- Provide examples of biomimicry
- Show videos or direct students to websites with examples
- Discuss how nature’s systems can help solve human challenges
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF BIOMIMICRY:
Biomimicry is the practice of studying nature to solve human problems in a sustainable way. It can have many advantages, including improved efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. However, there are also some potential drawbacks.
Advantages
- Sustainability: Biomimicry can help reduce resource consumption and environmental impact.
- Efficiency: Biomimicry can lead to more energy-efficient products.
- Innovation: Biomimicry can inspire new ideas and creative thinking.
- Cost-effectiveness: Biomimicry can reduce material costs by focusing on shape rather than material.
- Durability: Biomimetic materials can be more durable and have properties like strength, flexibility, and self-healing.
Drawbacks
- Unpredictability: The outcome of biomimicry can be unpredictable.
- Limited understanding of nature: Our understanding of nature is limited, which can be a drawback to biomimicry.
- Technical and practical barriers: There can be technical and practical barriers to applying biomimicry.
- Respecting nature’s rights and values: There can be challenges around respecting nature’s rights and values.
KEY TECHNOLOGIES:
Biomimicry is a method of innovation that uses nature’s design principles to create new technologies. Some examples of biomimicry technologies include:
- Velcro: Inspired by the cocklebur plant’s seed pod, which hooks into animal fur
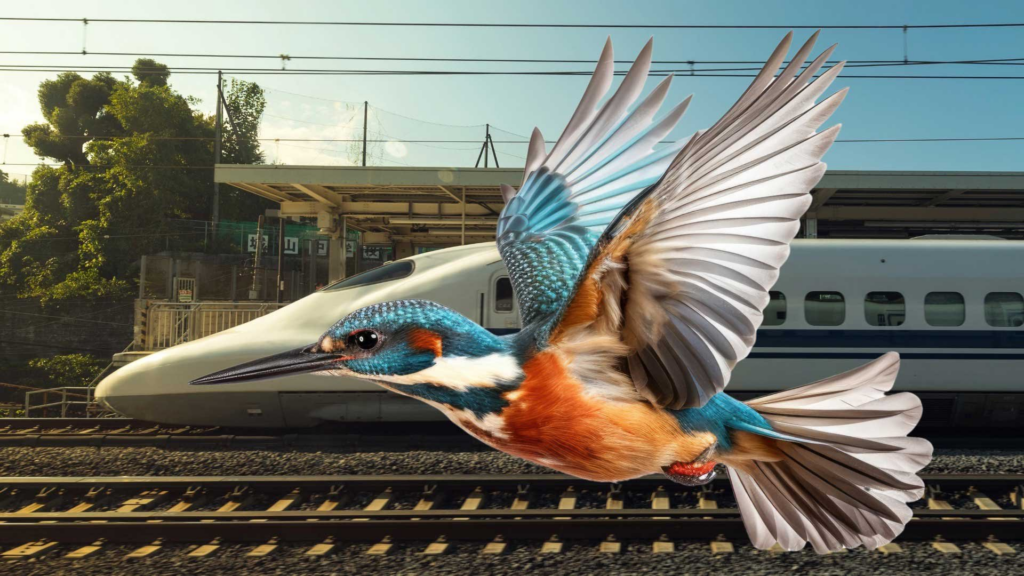
- Shinkansen: The aerodynamic Japanese train’s beak-shaped nose is inspired by the kingfisher, which travels between air and water with little splash
- Self-cleaning surfaces: Inspired by lotus leaves, these surfaces minimize water and chemical use
- Solar panels: Inspired by photosynthesis
Other examples of biomimicry include: Down feather insulation, Termite mound cooling, Humpback whale wind turbines, Beetle water collection, and Spider web glass.
Biomimicry can be applied in many areas, including engineering, architecture, medicine, and robotics.
How biomimicry works
Biomimicry is also known as biomimetics, bio design, or nature-inspired innovation. It’s an interdisciplinary field that aims to create healthier, greener, and more sustainable products.
Benefits of biomimicry
Biomimicry can help make human productions more efficient, resilient, and sustainable.

USES OF BIOMIMICRY:
Biomimicry is the practice of imitating nature to solve human problems. It has applications in many fields, including architecture, engineering, textiles, and medicine.
Examples of biomimicry
- Wind turbines: The shape of humpback whale fins inspired the design of wind turbine blades, which helps the turbines spin more efficiently
- Textiles: Textiles inspired by lotus leaves are self-cleaning and stain-resistant, while those inspired by spider silk are strong and elastic
- Buildings: Energy-efficient building designs reduce energy consumption
- Coatings: Down feathers are used to insulate winter coats
- Medical: Biomimetic materials are used in medical health
- Aerospace: Biomimetic materials are used in aerospace
- Agriculture: Biomimetic materials are used in agricultural planting
Benefits of biomimicry
- Biomimicry can help create sustainable systems
- Biomimicry can help create products and systems that eliminate waste and create a circular economy
- Biomimicry can drive innovation and creativity

REFETRENCE:

