WATER PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES:
INTRODUCTION:
Water purification technologies remove contaminants from water to make it safe to use. These technologies include physical separation, chemical processes, and biological processes.
Physical separation
- Filtration: Removes suspended particles, bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants
- Thermal distillation: A water purification technology
- Membrane separation: A technology that uses semipermeable membranes to remove impurities
Chemical processes
- Disinfection: A water purification technology that uses chemicals to kill harmful bacteria
- Coagulation: A water purification technology that uses chemicals to remove contaminants
- Ion exchange: A water purification technology that uses chemicals to remove contaminants
Biological processes
- Slow sand filtration: A water purification technology that uses biological processes to remove contaminants
PROS AND CONS OF WATER PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES:
Water purification technologies offer several pros, including providing clean drinking water by removing contaminants, improving taste, and being cost-effective compared to bottled water; however, cons include potential high initial costs, the need for filter replacements, potential waste of water during purification, and may not always be effective against certain contaminants like viruses depending on the technology used.
Pros:
- Improved water quality: Effectively removes contaminants like chlorine, lead, bacteria, and sediments, resulting in cleaner and better tasting drinking water.
- Cost-effective: In the long run, using a water purifier can be cheaper than buying bottled water.
- Health benefits: Reduces the risk of waterborne diseases by removing harmful microorganisms.
- Environmental impact: Can reduce plastic waste associated with bottled water consumption.
- Taste enhancement: Carbon filters can significantly improve the taste of water by removing unwanted chemicals.
- Variety of options: Different technologies available to suit specific needs and water quality issues.
Cons:
- Initial cost: Buying and installing a water purification system can be a significant upfront investment.
- Maintenance and filter replacement: Regular filter changes are necessary to maintain optimal performance, which can add to ongoing costs.
- Water waste: Some technologies like reverse osmosis can waste a considerable amount of water during the purification process.
- Mineral removal: Depending on the technology, essential minerals may be removed from the water, which some people may prefer to retain.
- Potential for improper installation: Incorrect installation can compromise the effectiveness of the system.
- Not always effective against viruses: Some water purification technologies may not completely remove all types of contaminants, especially viruses.

ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF WATER PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGIOES:
Water purification technologies have many advantages, including improved taste and smell, and reduced risk of contamination. However, they also have some disadvantages, including waste water and limited effectiveness against viruses.
Advantages
- Improved taste and smell Water purifiers can remove chlorine and other impurities that can make water taste and smell bad.
- Reduced risk of contamination Water purification technologies can remove dangerous substances like lead, arsenic, and nitrates.
- Cost-effective Water purifiers can be a more cost-effective option than buying bottled water.
- Maintains water quality Water purification technologies can help ensure that water is safe to drink.
Disadvantages
- Wastes water Some water purification technologies can waste water during the purification process.
- Limited effectiveness against viruses Some water purification technologies are not very effective against viruses and bacteria.
- Requires regular cleaning and filter replacement Water filters need to be cleaned and replaced regularly to ensure they are effective.
- Initial installation costs The initial installation of some water purification technologies can be more expensive than other filtration methods.
USES OF WATER PURIFICATION TECHNOLOGIES:
Water purification technologies are used to make water safe to drink, and to meet the needs of industries and medical applications.
Drinking water
- Removes bacteria, viruses, parasites, algae, and fungi that cause diseases like cholera, typhoid, and diarrhea
- Helps prevent rectal and colon cancer
- Makes water safe for households, especially in areas with poor-quality tap water
Industrial applications
- Used in cooling, energy production, and manufacturing operations
Medical applications
- Used in medical and pharmacological applications for clean and potable water
Water purification technologies
- Ultrafiltration: Uses a membrane to remove large particles like impurities and germs
- UV treatment: Uses a UV lamp to transmit ultraviolet radiation that kills microorganisms
- Electrodeionization (EDI): Uses ion exchange resin and ion-selective membranes to remove ionized species in the water
- Activated carbon: Uses a granular substance to adsorb impurities in potable water
- Slow sand filtration: Uses sharp sand to remove turbidity, algae, and microorganisms
Water purification can take place on a large scale, such as for an entire city, or on a small scale, such as for individual households.
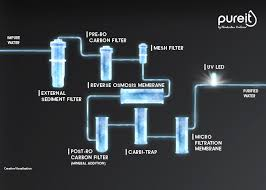
HOW IT WORKS:
Water purification technology typically involves passing water through a series of filters, using methods like sedimentation, mechanical filtration, activated carbon absorption, and sometimes disinfection with ultraviolet light, to remove contaminants like sediment, chemicals, bacteria, and other impurities, with the most common advanced method being “reverse osmosis” which forces water through a semi-permeable membrane to trap contaminants too large to pass through, leaving clean water behind;.
Key components of water purification systems:
- Sediment filter:Removes large particles like dirt and sand through a coarse mesh.
- Activated carbon filter:Absorbs organic compounds, chlorine, and odors using porous carbon material.
- Sand filter:Further removes smaller particles by passing water through a layer of sand.
- Reverse osmosis (RO) membrane: A semi-permeable membrane that only allows water molecules to pass through, filtering out dissolved minerals and contaminants.
- Ultraviolet (UV) light: Kills bacteria and other microorganisms by disrupting their DNA with ultraviolet radiation.
How it works:
- 1. Initial filtration: Water enters the system and passes through a coarse filter to remove large particles.
- 2. Carbon filtration: The water then flows through an activated carbon filter to absorb chemicals and odors.
- 3. Sedimentation: In some systems, water may be held in a tank to allow heavier particles to settle to the bottom.
- 4. Reverse osmosis (if applicable):Water is forced under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane, leaving behind dissolved solids.
- 5. Disinfection: Finally, the filtered water may be exposed to UV light to kill any remaining bacteria.